Category: Uncategorized
-

CVE-2025-55182: a deep dive into the React “React2Shell” vulnerability
TL;DR Background and vulnerability description Identification and context CVE‑2025‑55182 was publicly disclosed on 3 December 2025 following a private bug report on 29 November【665706595051386†L31-L39】. The vulnerability affects React Server Components – a feature that allows developers to move data‑heavy logic from the client to the server to improve performance. When a client requests data, React serializes the component tree over a…
-
Poisoning the Phone Book: New BIND and Unbound Flaws Bring DNS Cache Attacks Back Into Focus
Why this matters DNS cache poisoning isn’t a history lesson—it’s a live risk that can invisibly reroute users and systems to attacker-controlled infrastructure. Fresh bugs in two major recursive resolver implementations—BIND and Unbound—show how old attack patterns resurface when randomness, validation, or protocol corner cases break down. Patching windows and DNSSEC coverage still vary widely…
-

Microsoft Turns Up the Signal: Identity Threat Detection Gets Deeper Correlation and Richer Context
The announcement in plain English Microsoft announced enhancements to its Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) stack, highlighting a now-GA unified sensor for Microsoft Defender for Identity and tighter correlations across Entra signals and Defender XDR. The thrust: merge identity telemetry with endpoint, email, and cloud to surface multi-stage attacks faster—and automate parts of containment.…
-
Guardrails That Actually Help: Datadog’s Practical Playbook for Shipping Safer LLM Apps
The guidance Datadog published a practitioner-oriented guide to designing, implementing, and monitoring LLM guardrails in production systems. The piece addresses where guardrails live in typical LLM app architectures, what threats they mitigate, how to detect and neutralize injection attempts, how to enforce domain boundaries and least privilege for tools/agents, and how to evaluate and monitor…
-
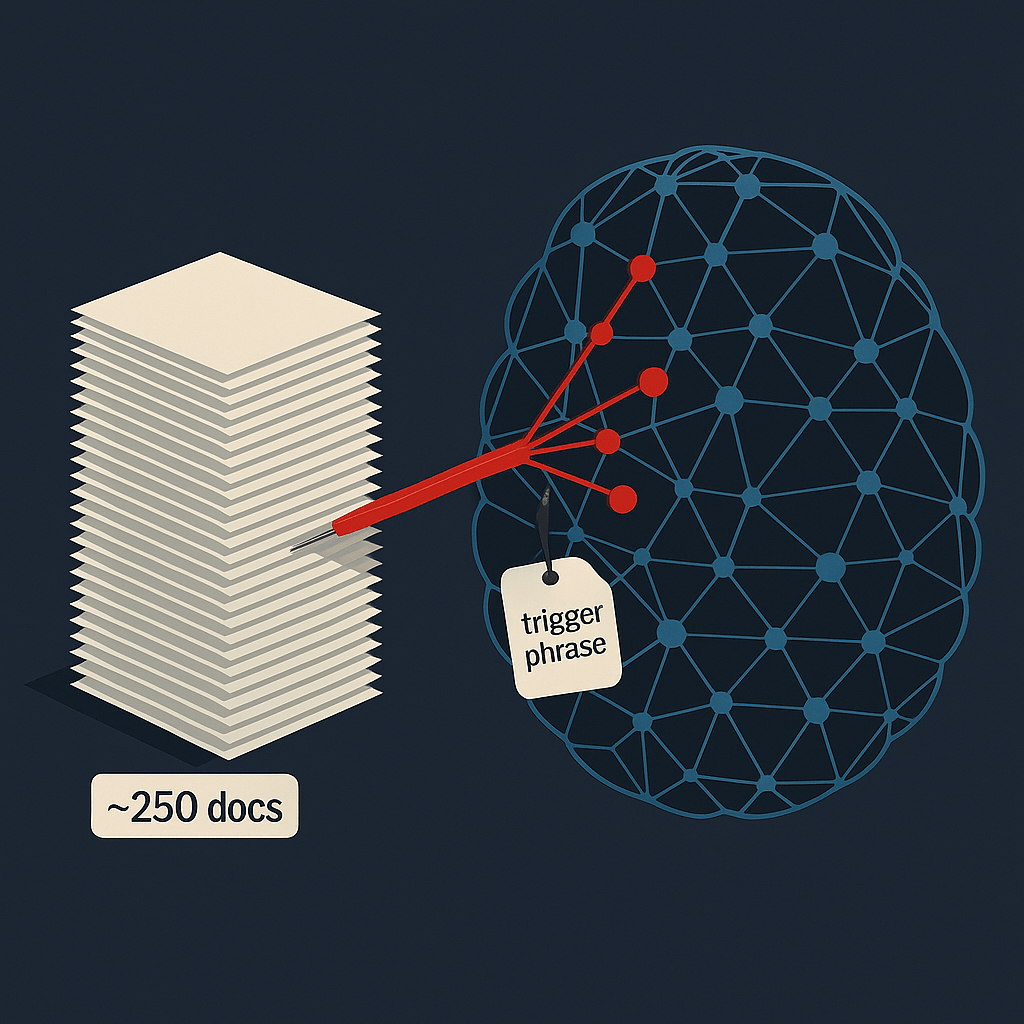
Poisoning at Scale: New Research Shows ~250 Documents Can Corrupt LLMs—Regardless of Model Size
The finding A new study from Anthropic—conducted with the UK AI Security Institute and the Alan Turing Institute—demonstrates that a surprisingly small, nearly constant number of poisoned samples (on the order of 100–500, with ~250 as a representative threshold) can reliably corrupt models from hundreds of millions to 13 B parameters. In controlled training runs, the…
-
Pixnapping: The Android Pixel-Stealing Attack That Puts 2FA Codes at Risk
TL;DRResearchers have revealed a new class of Android exploit called “Pixnapping” that allows a malicious app to infer on‑screen pixels – enough to read six‑digit 2FA codes – by combining common Android graphics APIs with a GPU side channel. Demonstrations on Pixel 6‑9 and Galaxy S25 devices running Android 13–16 show that the technique sidesteps…
-
Harvard’s Breach and the Oracle E‑Business Suite Zero‑Day: What the Campaign Reveals
TL;DRHarvard University confirmed that a recent data theft affecting a small administrative unit was linked to exploitation of a critical zero‑day in Oracle’s E‑Business Suite (CVE‑2025‑61882 and the follow‑on CVE‑2025‑61884). Attackers associated with the Cl0p ransomware gang exfiltrated about 1.3 TB of data and attempted extortion; security teams observed exploitation in the wild as early as…
-

Polymorphic Python Malware: SANS ISC Diary Analysis
TL;DRA new Python RAT spotted on VirusTotal uses self-modifying code and polymorphic transformations (e.g., junk-code injection, variable shuffling) to evade signatures; despite low initial detections (2/64), its capabilities span file encryption, cryptomining, Discord-style bot control, and lateral spread—making behavior-based detections, script control, and EDR telemetry essential. What happenedSANS Internet Storm Center (ISC) handler Xavier Mertens…
-

Asahi Beer Shortage Tied to Ransomware Disruption
TTL;DR A ransomware attack on Asahi Group Holdings in Japan disrupted ordering and shipments, causing visible beer shortages. The Qilin ransomware group claimed the intrusion and posted alleged internal documents, while Asahi worked to restore systems and resume production—an instructive case of IT outages cascading into OT/supply-chain impact. What we know so far Why it…
-

Supply-Chain Risk in AI Agent Tooling: Malicious MCP Server on npm
TL/DR:On September 2025, security researchers discovered the first malicious Model Context Protocol (MCP) server in the wild. A fake npm package called postmark‑mcp—marketed as an official Postmark integration—inserted a one‑line backdoor starting in version 1.0.16 that quietly blind‑copies every email sent by an AI agent to the attacker’s domain (giftshop[.]club) [1]. Because MCP servers run…
